
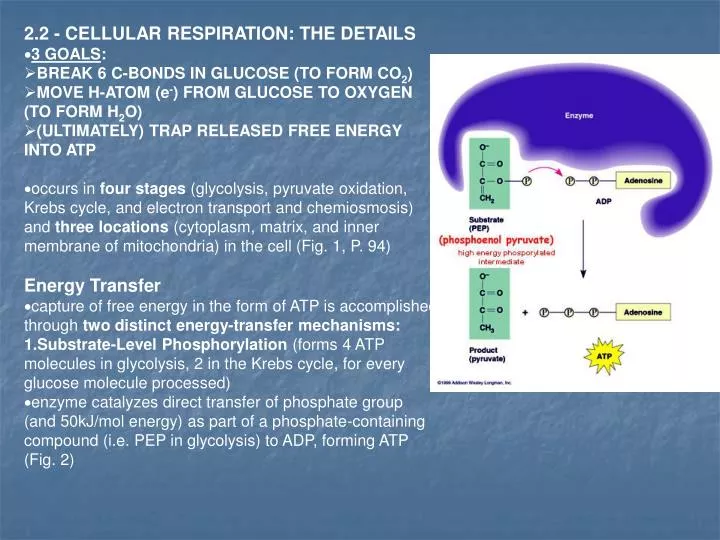
Photosynthesis is a process in photoautotrophs that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds in the presence of sunlight. Reaction takes places in presence of chlorophyll.ĭefinitions of photosynthesis and respiration No catalyst is required for respiration reaction. Occurs in plants, protista (algae), and some bacteria.Ĭatalyst - A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction Occurs in all living organisms (plants and animals). Electrochemical gradient creates energy that the protons use to flow passively synthesizing ATP. High H+ concentration in the thylakoid lumenĮlectron transport chain. H+ gradient across thylakoid membrane into stroma. High H+ concentration in the intermembrane space. H+ proton gradient across the inner mitochondria membrane into matrix. Glucose is broken down into water and carbon dioxide (and energy).Ĭarbon dioxide and water combine in presence of sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen.Ĥ stages: Glycolysis, Linking Reaction (pyruvate oxidation), Krebs cycle, Electron Transport Chain (oxidative phosphorylation).Ģ stages: The light dependent reaction, light independent reaction. Releases energy in a step wise manner as ATP molecules Oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released.Ĭarbon dioxide is absorbed and oxygen is released. The production of organic carbon (glucose and starch) from inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide) with the use of ATP and NADPH produced in the light dependent reaction glycolosis: breaking down of sugars occurs in cytoplasm Krebs Cycle: occurs in mitochondria requires energy Electron Transport Chain- in mitochondria converts O2 to water.

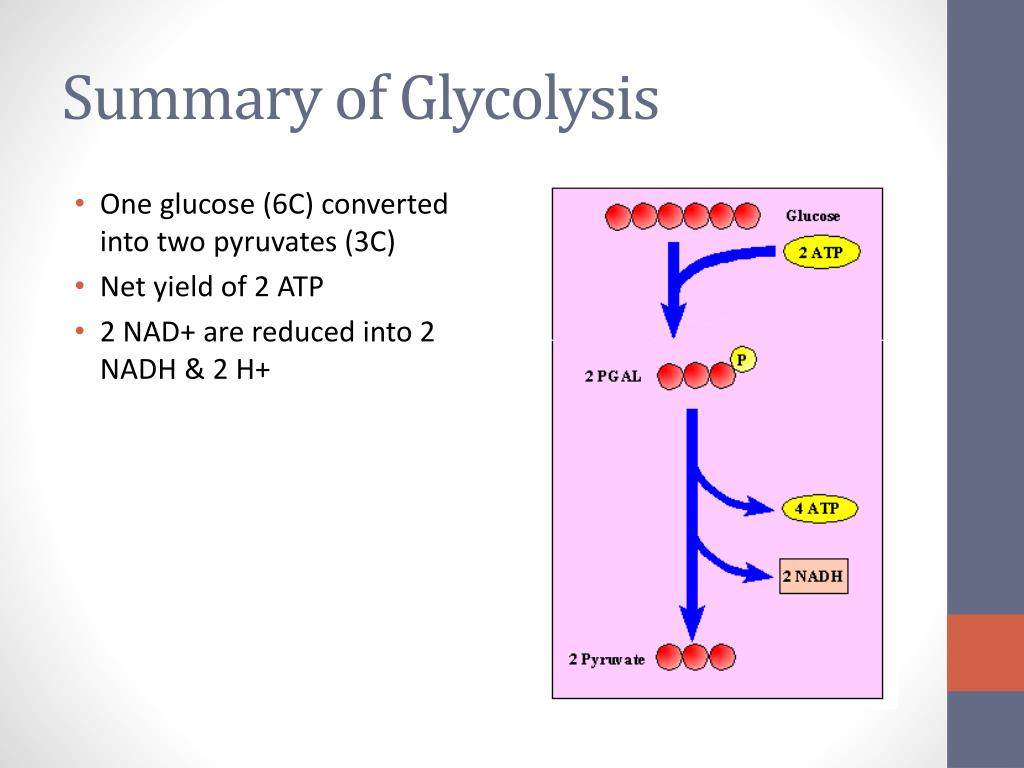
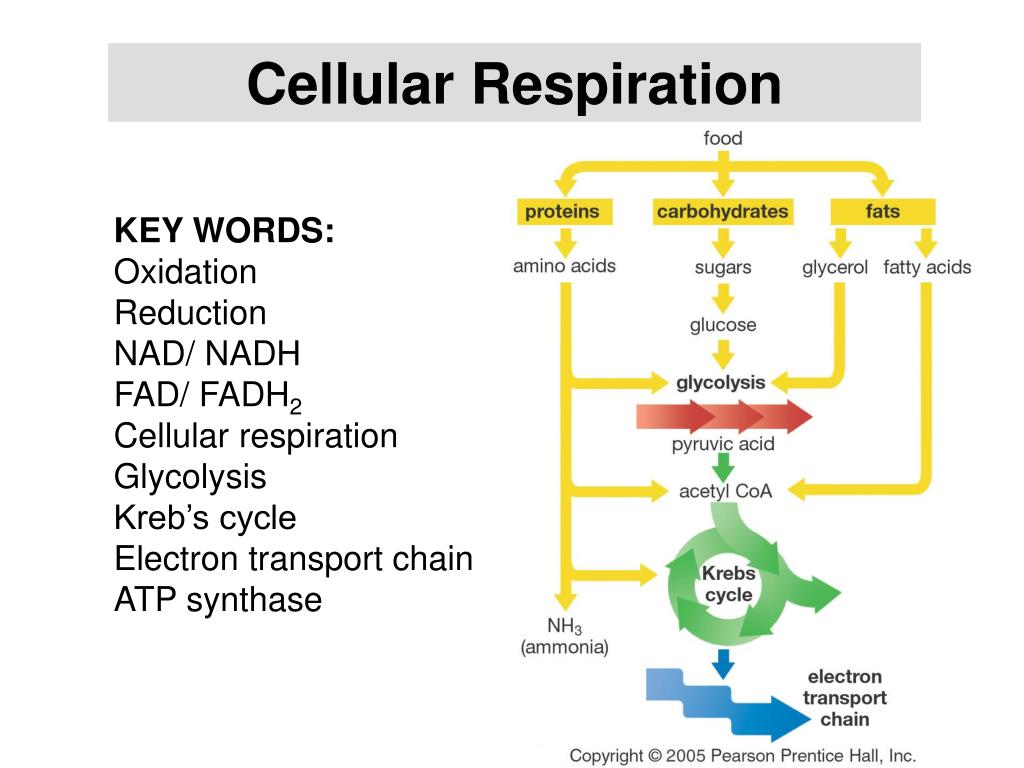
Production of ATP via oxidation of organic sugar compounds. Sunlight not required cellular respiration occurs at all times.ĦO2 + C6H12O6 -> 6CO2 +6H2O + ATP (energy)ĦCO2 + 12H2O + light -> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H20 Yes theoretical yield is 38 ATP molecules per glucose but actual yield is only about 30-32. Comparison chart Cellular Respiration versus Photosynthesis comparison chart


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
